| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||||
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 |
- OAuth 카카오
- node.js path
- css기초
- express.static
- 라우터 분리
- JWT 하드코딩
- JWT 만들어보기
- next 매개변수
- 세션으로 로그인 구현
- mysql wsl
- cookie-parser 만들어보기
- useEffect clean up
- ws 라이브러리
- express router
- FormData()
- 비동기파일업로드
- 블록 만들기
- express session
- 라우터와 미들웨어
- 라우터미들웨어 분리
- useContext
- 시퀄라이즈 기본설정
- Uncaught Error: could not find react-redux context value; please ensure the component is wrapped in a <Provider>
- nodejs파일업로드
- javascript기초
- 아이디 중복체크기능
- 라우트 매개변수
- JWT 로그인 기능 구현
- express실행
- buffer.from
- Today
- Total
즐코
[vue] methods / computed / watch 본문
누가 vue에서 헷갈리는 프로퍼티가 있냐고 물어본다면 나는 computed 와 watch 라고 말할거다.
그래서 공부하는 김에 정리해두고 적재적소에 쓰고자 한다.
우선 기본적으로 <template> 내에는 많은 로직이 직접적으로 들어가면 복잡해 보일 뿐만 아니라 해당 조건이 반복적으로 쓰인다면 유지보수가 어렵다. (아래의 예시) 그래서 methods / computed / watch와 같은 속성이 존재한다.
<template>
<p>Has published books:</p>
<span>{{ author.books.length > 0 ? 'Yes' : 'No' }}</span>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
author: {
name: 'John Doe',
books: [
'Vue 2 - Advanced Guide',
'Vue 3 - Basic Guide',
'Vue 4 - The Mystery'
]
}
}
}
}
</script>
computed
위의 예시를 computed를 사용해서 리팩토링했다.
데이터를 가공하는 등의 복잡한 연산은 뷰 인스턴스 내부에서 하고 최종적으로 html 상에는 데이터를 표현만 하는 것이 중요하다.
우선은 간단하게 데이터 연산을 정의하는 영역을 computed라고 생각하면 된다.
다른 state(데이터)에 의존하는 데이터를 정의할 때 computed를 쓴다!
- 자동 연산 : computed 속성에서 사용하고 있는 data 속성값이 변경되면 자동으로 다시 연산해준다.
- 캐싱 효과 : 동일한 연산을 반복해서 하지 않고 연산의 결과값을 미리 저장하고 있다가 필요할 때 불러온다.
=> 데이터가 변경되지 않는 한 이전의 계산값을 가지고 있다.(캐싱하고 있다)
=> 즉, 화면이 리렌더링되어도 같은 값을 굳이 다시 계산하지 않고 이전 값을 가져다 쓴다.
<template>
<p>Has published books:</p>
<span>{{ publishedBooksMSg }}</span>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
author: {
name: 'John Doe',
books: [
'Vue 2 - Advanced Guide',
'Vue 3 - Basic Guide',
'Vue 4 - The Mystery'
]
}
}
},
computed : {
publishedBooksMsg() {
return this.author.books.length > 0 ? 'Yes' : 'No'
}
}
}
</script>
computed 속성 vs. methods 속성
methods 속성 : 호출할 때만 내부 함수들이 돌아간다 == 수동적 데이터 갱신
computed 속성 : 해당 속성에서 쓰이는 data값이 바뀌면 자동적으로 수행된다 == 능동적 데이터 갱신
아래의 코드와 gif를 보면, computed와 methods의 큰 차이를 알 수 있다.
- computedCount는 오로지 countComputed가 변경될때만 실행된다.
- 하지만, methodsCount()는 computedCount가 실행되면 화면상의 데이터가 바뀌기 때문에 자신과 연결된 countMethods가 바뀌는게 아님에도 실행된다. 즉, methods는 data가 변경되고 나서 가상 돔으로 다시 화면을 그리고 나면 실행되는 단계인 update 사이클이 동작했을 때 함수를 실행해버린다. 따라서 간단한 연산만을 하고, 템플릿 코드의 가독성을 위해서라면, 아래 경우들을 제외하고선 computed를 쓰는 게 좋다.
computed 를 못 쓰는 경우
1/ computed는 인자를 받지 않는다. 따라서 인자를 넣어서 데이터를 변경해야할 경우엔 methods를 써준다.
2/ HTTP요청과 같은 통신 코드는 넣지 않는다. 이런건 watch나 methods에 넣는 게 적합하다.
<template>
<div>
<p>computed : {{ computedCount }}</p>
<input type="button" value="+" @click="countComputed++" />
<input type="button" value="-" @click="countComputed--" />
<p>methods : {{ methodsCount() }}</p>
<input type="button" value="+" @click="countMethods++" />
<input type="button" value="-" @click="countMethods--" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
countComputed: 0,
countMethods: 0,
};
},
computed: {
computedCount() {
console.log("computed 연산");
return this.countComputed;
},
},
methods: {
methodsCount() {
console.log("methods 연산");
return this.countMethods;
},
},
};
</script>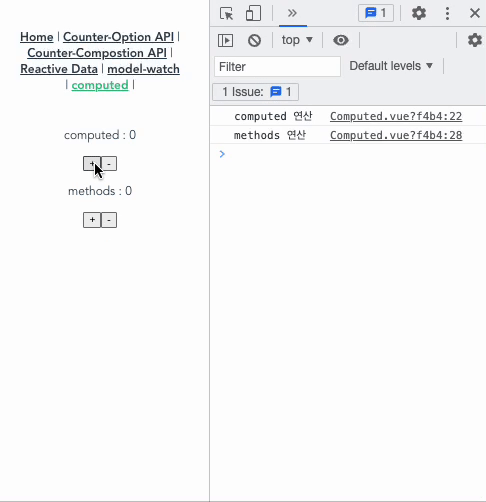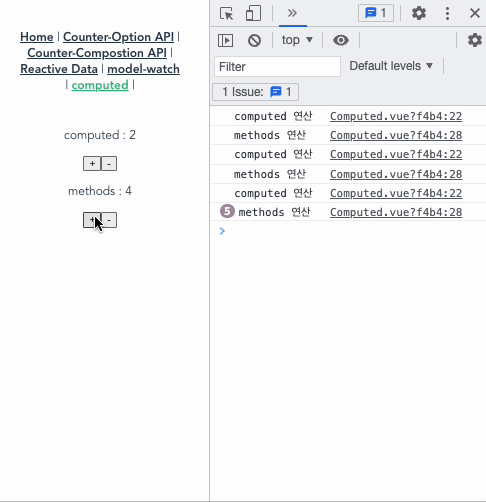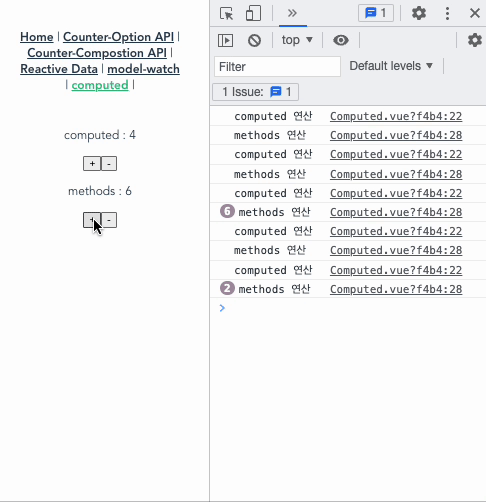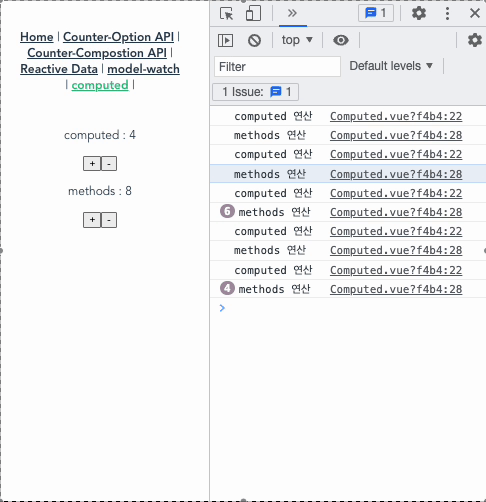
<추가적인 computed의 캐싱효과에 대한 예제>
똑같은 computed 가 2개 있을 경우, 하나만 연산하고 다른 하나는 캐싱해서 쓴다.
확인을 위해 아래 코드 상에서 computed에서도 콘솔을 찍고 method 상에도 콘솔을 찍어봤는데, computed는 캐싱효과로 인해 두번 가져다 써도 한 번만 돌아간다.
<template>
<div class="container">
<h4>count: {{ count }}</h4>
<h4>count: {{ count }}</h4>
<h4>double count computed: {{ doubleCountComputed }}</h4>
<h4>double count computed: {{ doubleCountComputed }}</h4>
<h4>double count method: {{ doubleCountMethod() }}</h4>
<h4>double count method: {{ doubleCountMethod() }}</h4>
<button @click="count++">Add one</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';
export default {
setup(){
const count = ref(1);
const doubleCountComputed = computed(()=>{
console.log('computed');
return count.value*2;
})
const doubleCountMethod = () => {
console.log('method');
return count.value*2;
}
return {
doubleCountComputed,
doubleCountMethod,
}
}
}
</script>
computed와 비슷한 watch는 또 어떤 케이스에서 써야할까
watch
watch도 연동된 데이터가 변경되면 이를 자동으로 감지하는게 computed와 매우 비슷하다.
여러 블로그들을 참고한 결과 아래와 같은 차이를 가지고 있다.
- computed : 반응형 getter / 연동된 데이터를 계산해서 보여주는 것
- watch : 반응형 콜백 / 연동된 데이터가 변경되면 다른 작업(콜백함수)을 실행시키는 것
watch는 기본적으로 아래와 같이 사용한다.
// msg라는 데이터가 변경될때 마다 watch에 정의한 콜백함수가 실행된다.
// 첫번째인자(newVal): 새로운 값, 두번째 인자(oldVal): 예전 값
<template>
<div>{{ msg }}</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return {
msg: 'hello world'
}
},
watch: {
msg: function(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log(newVal);
}
}
}
</script>
1. watch 속성에 methods 함수를 연결
: 함수로직은 methods 속성에서 따로 작성해주고, 이를 해당 데이터에 매칭해주는 방식도 쓴다.
<script>
export default{
data(){
return {
msg: 'hello world'
}
},
watch: {
'msg': 'logMsg'
},
methods: {
logMsg() {
console.log(this.msg);
}
}
}
</script>
2. handler(), immediate 속성 사용
- handler : 연동된 데이터가 바뀔 때 실행되는 함수 (newVal, oldVal 인자를 가진다)
- immediate : true 일 경우 컴포넌트가 생성되자마자 handler 함수를 즉시 실행해준다.
<script>
export default{
data(){
return {
msg: 'hello world'
}
},
watch: {
'msg': {
handler(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log(newVal);
},
immediate: true
}
},
}
</script>
watch - $route(to, from)
보통 상위 컴포넌트에서 route path가 바뀌면서 하위컴포넌트가 변경될때 라우터의 변경을 감지하면서 뭔가를 실행할때 아래와 같은 코드를 많이 쓴다. route값(경로)이 바뀜에 따라 해당 함수가 돌아간다.
<script>
export default{
watch: {
$route(to, from) {
console.log('to', to); // to : 이전 경로 - 디테일은 아래 확인
console.log('from', from); // from : 바뀐 경로 - 디테일은 아래 확인
if(to.path != from.path) {
// route path가 바뀔 때마다 할일들 작성..(axios 요청 해도됨!)
}
}
}
}
</script>$route(to, from)의 to, from을 찍어보면 아래와 같다. (/counter -> /counter2 로 이동)

computed 속성 vs. watch 속성
템플릿 내의 값이 data와 종속되었을 때 computed를 사용하는 게 유리하다.
computed는 값이 캐싱되어서 리렌더링 됐을 때 같은 값이 들어왔다면 연산하지 않는다. 반면, watch는 같은 값이여도 연산을 다시 한다.
- computed : 컴포넌트가 리렌더링이 많이 되는데 값이 바뀔 일이 없을 때 꼭 쓰기
- watch : 감시하는 값이 변경된 시점에서 내가 원하는 액션을 취하고 싶을때 (api call 이나 router.push()같은 경우)
'Vue' 카테고리의 다른 글
| json-server (0) | 2022.12.29 |
|---|---|
| [vue] props로 전달할 데이터에 대하여 (0) | 2022.12.11 |
| [vue] vue에서의 axios 요청 / axios.create() / interceptors (1) | 2022.11.26 |
| [vue] .env 설정 (0) | 2022.11.22 |
| [vue] 라우팅 (0) | 2022.11.14 |




